Chapter
03 Use It
1).
The following three tables make up a simple reservation system for a small
campground. The database should allow for a camper to make multiple
reservations for future dates and for a camping spot to have several
reservations for upcoming visits.
2). The
following three tables make up a simple reservation system for a small
campground. The database should allow for a camper to make multiple
reservations for future dates and for a camping spot to have several
reservations for upcoming visits.
Quiz:
Chapter 03 The Relational Database Model
1). Which
of the following is not a valid characteristic of a relational table?
|
a. It is perceived as a two-dimensional structure
composed of rows and columns.
|
|
|
|
b. The order of the rows and columns is irrelevant to
the DBMS.
|
|
|
|
c. Each table column represents an attribute and each
column has a distinct name.
|
|
|
|
d. All values
in a column may have different data formats.
|
|
2). Which
of the following statements best describes a functional dependency?
|
a. The value
of one or more attributes determines the value of one or more other
attributes.
|
|
|
|
b. The condition in which each row in the table is
dependent on any subset of the key.
|
|
|
|
c. The value of an attribute determines the value of
one or more other attributes.
|
|
|
|
d. The data type of an attribute determines the data
type of another attribute.
|
|
3). Which
of the following is not a legitimate DB key in a relational model?
4). Which
of the following statements best defines the purpose of entity integrity?
|
a. Lacking a primary key, it enables each row to
identify other rows in other tables.
|
|
|
|
b. It secures the null key in the absence of any
data.
|
|
|
|
c. It
guarantees each entity has a unique value for the primary key and that
there are no null key values.
|
|
|
|
d. It validates each row will have a value
identifying foreign key values in other tables.
|
|
5). Dr. Codd published a list of 12 relational database rules
in 1985; which of the following is not a valid rule?
|
a. Every value in a table is guaranteed to be
accessible through a combination of table name, primary key value, and
column name.
|
|
|
|
b. The database must support set-level inserts,
updates, and deletes.
|
|
|
|
c. Nulls must be represented and treated in a
systematic way, independent of data type.
|
|
|
|
d.
Any database view that is theoretically updatable must be updated outside
of the database structure.
|
|
6). Which
of the following best describes an index?
|
a. An index is
an orderly arrangement used to logically access rows in a table.
|
|
|
|
b. It is a variable for holding database relation
data, not the relation itself.
|
|
|
|
c. It has an attribute with a value that determines
the value of other rows.
|
|
|
|
d. An index is an orderly arrangement used to
physically access rows in a table.
|
|
7). A
composite entity is also referred to as a _____ entity.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8). The proper use of foreign keys _____
data redundancies and the chances that destructive data anomalies will
develop.
|
9). Which of the following statements best defines a data
dictionary?
|
a. The data dictionary provides a detailed
description of all entities in the database created by the user and
designer.
|
|
|
|
b. The data
dictionary provides a detailed description of all tables in the database
created by the user and designer.
|
|
|
|
c. The data dictionary provides a detailed
description of all tables in the database created by the developer and
designer.
|
|
|
|
d. The data dictionary provides a
detailed description of all entities in the database created by the
developer and designer.
10). Which of
the following is not a valid relational set operator?
|
|
Chapter 04 Use It
1. Wynwood District
Provide all appropriate connectivities
using the following business rules:
- An artist owns at least one artwork but a given
artwork is owned by one artist only.
- An artwork is classified into one art style only.
Each art style must have at least one artwork.
- An art collector may review/rate more than one
artist.
- An art collector can purchase many artworks but a
purchase order is placed by one art collector only.
1. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 1
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 2
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 3
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 4
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 5
Hide Feedback
Correct
6. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 6
Hide Feedback
Correct
7. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 7
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Book Club
Provide all appropriate connectivities
using the following business rules:
- A reader follows at least one author and an author may
be followed by many readers.
- A reader may be part of many reading groups and a
reading group has at least one reader.
- An author wrote at least one book and a book may
have been written by many authors.
- A book is printed by one publisher only and a publisher
prints many books.
1. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 1
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 2
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 3
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 4
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 5
Hide Feedback
Correct
6. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 6
Hide Feedback
Correct
7. Provide the appropriate connectivity
using the above business rules for number 7
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Tech Support
Using Crow’s Foot Model, provide all
appropriate cardinalities using the following business rules:
- Each staff is part of one of the five IT Teams
(Helpdesk, Server, Network, Desktop, Email) and a team may have many staff
members.
- Each user will have the ability to submit as many
tickets as needed, and each ticket must be tied to a single user.
- Each ticket is assigned to at least one topic area
but no more than three topics per ticket. A topic can include many
tickets.
1. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 1
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 2
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 3
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 4
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 5
Hide Feedback
Correct
6. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 6
Hide Feedback
Correct
7. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 7
Hide Feedback
Correct
8. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate cardinalities using the above business rules for number 8
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Traffic Ticket
Using Chen Model with the (min, max)
notation, provide all appropriate cardinality using the following business
rules:
- A vehicle is owned by one and only driver. A driver
owns at least one vehicle.
- A law enforcement officer issues many fine tickets
and a motorist may have received many fine tickets.
1. Using Chen Model with the (min, max)
notation, provide the appropriate cardinality using the above business rules
for number 1
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Using Chen Model with the (min, max)
notation, provide the appropriate cardinality using the above business rules
for number 2
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Using Chen Model with the (min, max)
notation, provide the appropriate cardinality using the above business rules
for number 3
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Using Chen Model with the (min, max)
notation, provide the appropriate cardinality using the above business rules
for number 4
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Using Chen Model with the (min, max)
notation, provide the appropriate cardinality using the above business rules
for number 5
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Heath Clinics
Using Crow’s Foot Model, provide all
appropriate connectivities using the following business rules:
- A physician works at one and only one clinic
location and a clinic has at least one physician worker.
- A physician can prescribe one or more medications to
several patients and a patient can obtain many prescriptions from several
physicians.
1. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 1
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 2
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the appropriate
connectivity using the above business rules for number 3
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 4
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 5
Hide Feedback
Correct
6. Lead Management
Using Crow’s Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the following business rules:
- A property is owned by a single homeowner but a
homeowner may have multiple properties.
- A property may be purchased by one single buyer but
a buyer can purchase many properties.
- A real estate agent may manage more than one
property at a time but a property is managed by one manager only.
1. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 1
Hide Feedback
Correct
2. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 2
Hide Feedback
Correct
3. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 3
Hide Feedback
Correct
4. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 4
Hide Feedback
Correct
5. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 5
Hide Feedback
Correct
6. Using Crow's Foot Model, provide the
appropriate connectivity using the above business rules for number 6
Hide Feedback
Correct
Quiz: Chapter 04 Entity Relationship (ER) Modeling
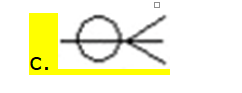
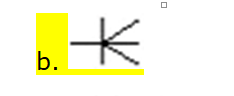
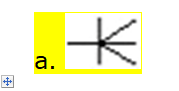
1).When working
with entity relationship models (ERM), which of the following is not a valid
statement regarding an entity?
|
a. An entity
is an object of interest to the end designer.
|
|
|
|
b. In the Chen, Crow's Foot, and UML notations, an
entity is represented by a rectangle that contains the entity name.
|
|
|
|
c. An entity refers to the entity set and not to a
single entity occurrence.
|
|
|
|
d. The ERM refers to a table row as an
entity instance or entity occurrence.
|
|
2). In an
entity relationship model (ERM), attributes are characteristics of entities.
Which of the following statements best describe an optional attribute?
|
a. An optional
attribute is an attribute that does not require a value and can be left
empty.
|
|
|
|
b. An optional attribute is an attribute that
requires a value and can be an optional key.
|
|
|
|
c. An optional attribute is an attribute that
requires a value and can be left empty.
|
|
|
|
d. An optional attribute is an
attribute that does not require a value and can be an optional key.
|
|
3). What type
of attribute allows for no more than one value?
|
a. Single-valued
attribute
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4). The CUSTOMER entity includes the
attributes CUST_LNAME, CUST_FNAME, CUST_PHONE, and CUST_PHONE_TYPE. The
CUST_PHONE_TYPE attribute stores the string "HOME, WORK, MOBILE,
OTHER". Which term best describes CUST_PHONE_TYPE?
|
|
|
|
|
c. Single-valued attribute
|
|
|
|
|
5). A derived attribute is an attribute
whose value is calculated (derived) from other attributes. What is not an
advantage of storing derived attributes in the database?
|
a. Can keep track of historical data
|
|
|
|
b. Uses CPU
processing cycles
|
|
|
|
c. Saves data access time
|
|
|
|
d. Data value is readily available
|
6). What type
of entity can exist in the database only when it is associated with another
related entity?
7). What
element expresses the specific number of entity occurrences associated with
an occurrence of a related entity?
8). A
relationship degree indicates the number of entities or participants
associated with a relationship. Which is not a valid relationship that's
specifically named?
|
|
|
|
|
c. Quarterly
relationship
|
|
|
|
|
9). Database
designers must often compromise design due to conflicting goals. What are
examples of contradictory goals in database design?
|
a. Primary key, composite key, and foreign key
|
|
|
|
b. Chen notation, Crow's Foot notation, and UML
notations
|
|
|
|
c. Design
standards, processing speed, and information requirements
|
|
|
|
d. Attributes, domains, and entities
|
|
10). While a relationship degree
indicates the number of entities associated with a relationship, which
relationship type is within a single entity type?
|
a. Recursive
relationship
|
|
|
|
|
|
c. Higher-order relationship
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quiz:
Chapter 05 Advanced Data Modeling
1). When looking into the extended entity relationship model
(EERM), which of the following statements is not valid about entity supertypes
and subtypes?
|
a. Entity supertype and subtype are based on a
hierarchical structure.
|
|
|
|
b. The entity supertype contains common
characteristics with subtype.
|
|
|
|
c. The entity
subtype contains common characteristics.
|
|
|
|
d. An entity supertype is a generic
entity type related to one or more entity subtypes.
|
|
2). In
an extended entity relationship, which of the following statements is not valid
about inheritance?
|
a. Inheriting
the relationships of their supertypes means subtypes cannot have
relationships of their own.
|
|
|
|
b. Entity subtypes inherit all relationships in which
the supertype entity participates.
|
|
|
|
c. Entity subtypes inherit their primary key
attribute from their supertype.
|
|
|
|
d. Inheritance enables an entity subtype to inherit
the attributes and relationships of the supertype.
|
|
3). In
the extended entity-relationship model (EERM), which of the following
statements best describes the completeness constraint?
|
a. Partial completeness constraint means that every
supertype occurrence is a member of a subtype.
|
|
|
|
b. The completeness constraint specifies whether each
entity subtype occurrence must also be a member of at least one supertype.
|
|
|
|
c. Total completeness constraint means that every
subtype occurrence must be a member of at least one supertype.
|
|
|
|
d. The
completeness constraint specifies whether each entity supertype occurrence
must also be a member of at least one subtype.
|
|
4). Which
of the following statements is not valid when describing entity clustering?
|
a. An entity cluster is a "virtual" entity
type used to represent multiple entities and relationships in the ERD.
|
|
|
|
b. An entity cluster is formed by combining multiple
interrelated entities into a single, abstract entity object.
|
|
|
|
c. An entity cluster is considered
"virtual" or "abstract" because it is not an actual
entity in the final ERD.
|
|
|
|
d. An entity
cluster is a permanent entity used to represent multiple entities and
relationships, intended to simplify the ERD, and thus enhance its
readability.
|
|
5). Which
of the following statements best describes the essential characteristic of an
entity's primary key?
|
a. A primary key is the attribute or combination of
attributes uniquely identifying an entity's instance in an entity set.
|
|
|
|
b. The main function of the primary key is to
guarantee entity integrity and to "describe" the entity.
|
|
|
|
c. It has no intrinsic meaning; values for it can be
generated by the DBMS to ensure that unique values are always provided.
|
|
|
|
d. The main
function of the primary key is to guarantee entity integrity, not to
"describe" the entity.
|
|
6). The primary key is possibly the most essential
characteristic of an entity; which of the following is not a desirable
characteristic of a primary key?
7). What primary key is created by the database designer to
simplify the identification of entity instances?
8). Identify the statement that best defines time-variant
data.
|
a.
Time-variant data refers to data that changes over time; its history of
data changes must be maintained.
|
|
|
|
b. Time-variant data refers to data that changes over
time, with no history of data change tracking.
|
|
|
|
c. Time-variant data refers to data that does not
change over time.
|
|
|
|
d. Time-variant data refers to data
that was created redundantly.
|
|
9). Which
statement from the following describes specialization and generalization?
|
a.
Specialization is the top-down process of identifying lower-level, more
specific entity subtypes from a higher-level entity supertype.
Generalization is the bottom-up process of identifying a higher-level, more
generic entity supertype from lower-level entity subtypes.
|
|
|
|
b. Specialization is the top-down process of
identifying lower-level, more specific entity supertypes from a
higher-level entity subtype. Generalization is the bottom-up process of
identifying a higher-level, more generic entity supertype from lower-level
entity subtypes.
|
|
|
|
c. Specialization is the top-down process of
identifying lower-level, more specific entity supertypes from a
higher-level entity subtype. Generalization is the bottom-up process of
identifying a higher-level, more generic entity subtype from lower-level
entity supertypes.
|
|
|
|
d. Specialization is the top-down process of
identifying lower-level, more specific entity supertypes from a
higher-level entity subtype. Generalization is the bottom-up process of
identifying a higher-level, more generic entity supertype from lower-level
entity subtypes.
|
|
10). Which of the following statements describe a fan trap in
ERD design?
|
a. A fan trap occurs when there is one entity in two
1:1 relationships.
|
|
|
|
b. A fan trap occurs when there are more than two
entities in 1:M relationships.
|
|
|
|
c. A fan trap
occurs when there is one entity in two 1:M relationships to other entities.
|
|
|
|
d. A fan trap occurs when there is one
entity in two 1:1 relationships to other entities.
|
|

.png)
.png)


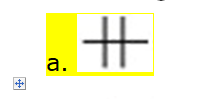





Comments
Post a Comment